This post may contain affiliate links, which means that we get commissions for purchases made through such links, at no additional cost to you. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Welcome to this comprehensive article where we talk about how thermal paper works. If you are as curious as we are, you may have wondered how thermal papers produce images without ink. Our team of experts looked into this, and we have answers for you.
How does thermal paper work? Thermal papers work by heat activation. When exposed to the hot pins of a thermal printer’s printhead, the heat activates dye pigments on the thermal paper. Upon activation, these pigments create images on the paper. That’s why thermal papers are called thermos-chromic (heat-sensitive, color-creating) papers. Thermal transfer papers, also a type of thermal labels, work by accepting heat-activated pigments from thermal ribbons. The heat from thermal printheads melts the ribbon pigment onto the plain thermal transfer paper.
“Thermal paper” is sometimes used to refer to both thermal papers (direct thermal papers) and thermal transfer papers. But these are two different types of papers used for two different thermal printing mechanisms. As you read on, we will show you how direct thermal papers work, as well as how thermal transfer papers work. We will also explain how to ensure that your thermal papers work well.
How Does Direct Thermal Paper Work?
Thermal papers are coated with special heat-sensitive dye pigments. These dye pigments remain latent until they are activated by heat. When the paper comes in contact with the hot pins of a thermal printer’s printhead, the color of the dye pigments becomes visible on the paper. This means that direct thermal papers must come in direct contact with the thermal printhead for images to appear. The printhead only applies heat on specific points on the paper where imprints should appear.
Thermal papers are made up of a heat-sensitive layer of dye pigments on a paper base (also called the substrate layer). This means that when you hold a direct thermal paper, what you are holding is more than just a paper. The paper base is carrying another layer of chemically active heat-sensitive pigments on it. This layer of heat-sensitive dye pigments creates imprints on the paper base when the dye pigments are activated by heat.
Some thermal papers also have a layer of protective coating on the pigment layer. This layer of protective coating, if present, offers some protection against certain elements that can damage the thermal paper or affect its imprints.
How Does Heat Create Images on Thermal Papers?
Heat activates the dye pigments on thermal papers to create images. But this activation can happen in one of two ways, depending on the type of dye coating on the thermal paper. Some dye pigments are hidden in microcapsules (very small capsules). The heat from thermal printheads bursts these capsules in certain parts of the paper and releases the dye. The released dye creates imprints on those specific parts of the thermal paper.
The pigment on some thermal papers contains a colorless dye, a color developer (that can react with the dye to change its color), and a solid solvent that separated the dye from the developer. The heat from thermal printheads melts the solvent in certain parts of the paper and allows the dye to react with the color developer. The dye changes color (usually to blue or black) on those specific parts of the thermal paper and creates imprints.
✅ Video – How Does Thermal Paper Work?
In this illustrative video, you will learn how heat creates images on thermal papers. This video explains the mechanism used by thermal papers that contain a colorless dye and a color developer. You will see how heat causes these two components to react and what happens when they react.
Why Are Direct Thermal Papers Monochromic?
The color of imprint a direct thermal paper will create depends on the color of dye pigments in it. So the reason why most direct thermal papers are monochromic is that they have only one color of dye pigment, usually black. Other common colors of monochromic direct thermal papers are blue and red.
A few direct thermal papers can print two or more colors, depending on how many colors of dye pigments they have. The different dye colors are usually activated by varying degrees of heat. So the measure of heat that the thermal printhead applies to different parts of the paper determines the color of dye pigment that will be activated there. Multi-color direct thermal papers require special direct thermal printers whose printheads can achieve color differentiation by applying varying degrees of heat.
How Does Thermal Transfer Paper Work?
Thermal transfer papers accept melted ink pigments from thermal ribbons. The printhead of a thermal transfer printer melts pigments from thermal ribbons onto a thermal transfer paper during printing. As such, thermal transfer papers do not come in direct contact with thermal printheads because they do not contain heat-sensitive pigments. Instead, the surfaces of thermal transfer papers are designed to accept melted ribbon pigments and retain them.
During thermal transfer printing, thermal ribbons form a buffer layer between the thermal printhead and the thermal transfer paper. One side of the thermal ribbon is in contact with the thermal printhead while the other is in contact with the thermal transfer paper. When the printhead applies heat to specific parts of the thermal ribbon, the ribbon pigment melts and sticks to the surface of the thermal transfer papers. Some ribbon pigments even diffuse into the surface of the thermal transfer paper to create a more permanent print.
Is Thermal Transfer Paper Also A Type of Thermal Paper?
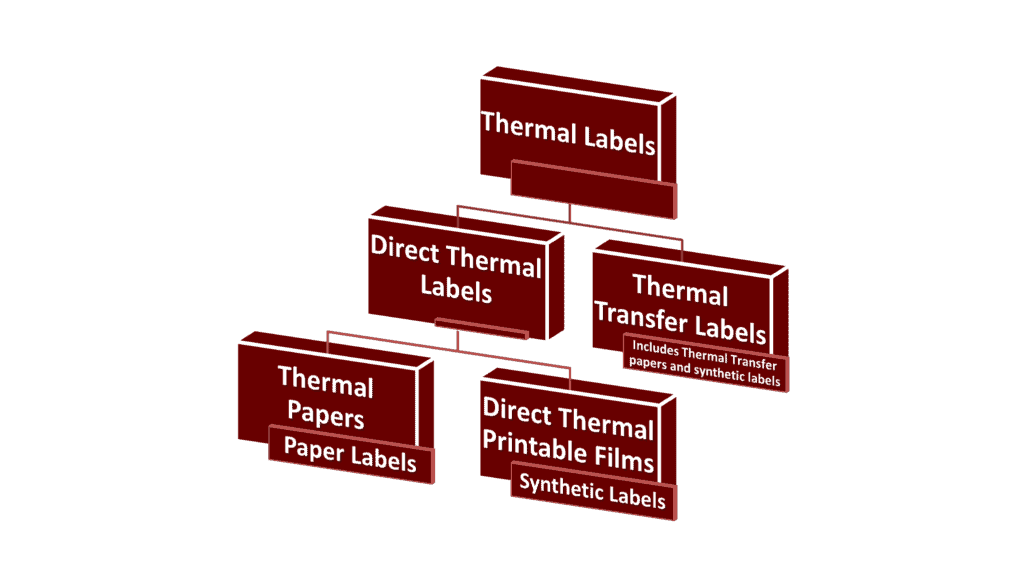
Thermal papers and thermal transfer papers are two different types of thermal labels (labels used for thermal printing mechanism). Thermal paper, if used strictly, refers to direct thermal papers – the heat-sensitive papers used for direct thermal printing. Thermal transfer paper, on the other hand, is another type of thermal label used for thermal transfer printing.
However, in common conversations, people don’t often make this distinction. They simply refer to both thermal papers and thermal transfer papers as thermal papers. This may be because many people confuse thermal label to mean the same thing as thermal paper.
All thermal papers are thermal labels. But not all thermal labels are thermal papers. Some thermal labels are thermal papers (for direct thermal printing) while some are thermal transfer papers (for thermal transfer printing). What’s more, thermal labels also include synthetic labels that have a synthetic substrate, like polyester, PVC, and polyethylene, rather than a paper substrate.
How to Make Thermal Papers Work Well?
The best practices for getting optimal results from thermal papers include storing the papers properly and testing them before using them. You should also print on thermal papers with the highest printer density (or heat) settings possible. This will help create sharp and durable imprints. What’s more, you should handle thermal papers carefully before, during, and after printing, and make sure not to rough-handle them.
Test the Paper before Use
Before you use any new thermal paper, make sure you test it with your printer first. You should get dark and clear images that meet the specific requirements for your printing application. This step is important because not all thermal printers are qualified for every thermal printer. If you are not buying the labels made by your printer’s manufacturer, you should ensure to test the label with your printer first.
Print with the Highest Heat Setting Possible
Your heat setting determines how much heat the printer’s printhead will apply to your thermal paper. If the heat setting is low, images can still appear on your thermal paper. But the chemical reaction that activated the dye pigments may be easily reversible. With the highest heat setting, the reaction is complete and cannot be reversed easily. This means your printed image will last longer.
Store the Thermal Papers Properly
Thermal papers are delicate and have strict storage requirements. Your storage area should be dry and cool; a place where the thermal papers will not be exposed to sunlight. You should also keep thermal papers away from petroleum products, alcohol, and other chemicals.
Handle the Thermal Papers Carefully
Avoid rubbing on thermal papers, especially on the side with the dye pigments. This can discolor the thermal papers. Scratches and scrapes also discolor thermal papers. You should take caution against these whenever you are handling thermal papers.
Related Questions
How Does Thermal Printer Work?
A thermal printer works by generating heat on its printhead and applying the heat on either thermal papers or thermal ribbons to create imprints. If it’s a direct thermal printer, it will apply heat directly on thermal papers to activate the dye pigments in them and create imprints. But if it’s a thermal transfer printer, it will apply heat on thermal ribbons and melt their pigments onto the surface of thermal transfer papers.
Thermal printers do not require ink or toners to create images. Their printheads simply generate heat to create imprints on thermal labels. As such, thermal printers work very quietly and are very fast.
Is Thermal Paper Dangerous?
Thermal papers often contain bisphenol A (BPA), which is known to be a toxic industrial chemical. BPA increases the risk of certain cancers, including prostate cancer and breast cancers. It has also been linked to increased risks of reproductive abnormalities and cardiovascular disease. What’s more, BPA also causes abnormalities of brain development in children.
However, occasional exposure to thermal papers will is not risky. The real people at risk of the toxic effects of BPA from thermal papers are those who are constantly exposed to thermal papers for an extended time. These include cashiers at stores that print thermal receipts all day long, every day.
How Long Does Thermal Paper Last Before It Fades?
The image life of thermal papers should be about 7-10 years. This means that your printed image should remain legible for about 7-10 years after the date of printing. But for this to happen, you must handle the paper correctly, print with the highest density possible, and store the printed thermal paper properly.
You can read our post, “How long do thermal labels last?” for more details on the lifespan of thermal labels.
Conclusion
In this post, we have explained how thermal labels work in detail. We believe that the information in this post has helped you solve the mystery of inkless printing. You now know the nitty-gritty of how thermal papers create images without ink.

